Cane Toad Hunting: Why Cruelty to Animals Is Never the Answer
Over the last 80 years, cane toads have colonised large swathes of tropical and subtropical Australia, leading some people to take up weapons, such as golf clubs or harsh chemicals, against these “invaders”. But poisoning or hitting any animal with a blunt instrument is cruel, and toad hunts are also a dangerous and ineffective form of population control.

How Did Cane Toads Get to Australia?
Cane toads were deliberately introduced to Australia from Hawaii in 1935 to combat the cane beetle, a native insect that feeds on sugar cane (which is itself an exotic species of grass first cultivated in the country at the time of the First Fleet).
This very profitable crop was severely affected by insect attacks – and rather than using pesticides, scientists suggested importing and introducing toads. There was little consideration of the feasibility of using these ground-based animals to control a population of airborne insects.
Furthermore, people failed to foresee that the amphibians would spread out from the cane fields – and that in the absence of their traditional predators, they would fall prey to native animals who generally have no resistance to the toxic secretions on the toads’ skin.
Despite their reputation as an invasive species, cane toads have had nothing to do with the extinction of any animal native to Australia.
Violence Is Never the Answer
None of this is the fault of the toads, who never asked to be brought to this country.
Yet some people head out at night wielding various weapons, including cricket bats and golf clubs, to beat them to death – with tragic results, and not just for the toads. In 2016, a 13-year-old Sunshine Coast boy went out hunting toads with friends and was accidentally hit with his friend’s golf club. He went into cardiac arrest and died a couple of days later.
Police called it a “terrible accident”, but it was certainly one that was waiting to happen, as young, impulsive children and hunting don’t mix.
In 2019, Queensland MP Bob Katter proposed a plan for children to become “cane toad bounty hunters” and shoot the animals with low-powered air rifles for 40 cents each.
Teaching kids to be cruel is psychotic, and it will inevitably lead some of them to act violently towards other animals and humans.
In the words of great moral philosopher Immanuel Kant:
“[H]e who is cruel to animals becomes hard also in his dealings with men”.
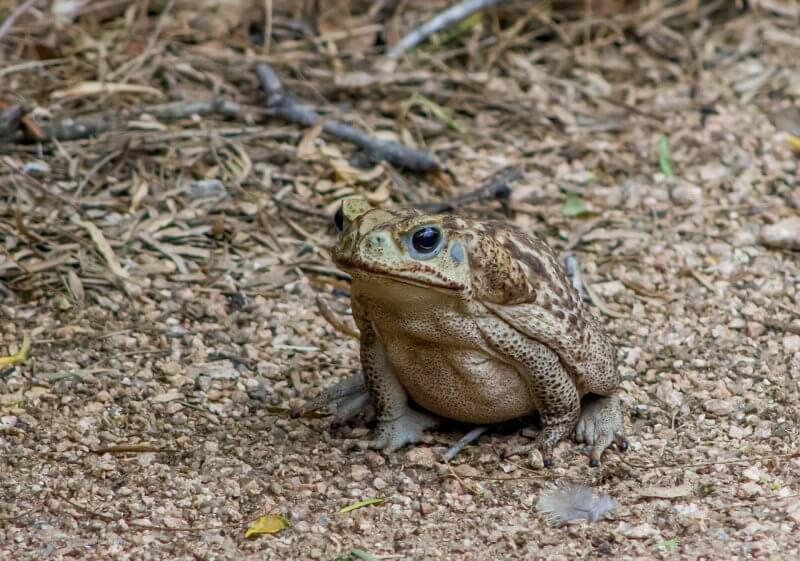

Native Frogs Are Often Mistaken as Toads
Cane toad hunting does not endanger only toads – native frogs are also at risk of being caught in the crossfire, since many people can’t tell the difference between the toads and the many native species of brown-coloured frogs.
More than one-third of cane toad sightings in New South Wales have turned out to be Australian frogs, according the Department of Primary Industries.
The endangered giant barred frog is particularly vulnerable to being identified incorrectly as a cane toad.
How to Humanely and Effectively Deal With Cane Toads
Culling has, in any case, repeatedly proved ineffective for cane toads. A single female toad can produce around 30,000 eggs in a single clutch – so the few animals that hunters inevitably miss can rapidly replace those removed. Such measures can even cause population booms, since killing or otherwise removing some individuals often improves conditions and the availability of food for those who remain. Also, since toads migrate, any purged area would most likely be re-invaded right away.
The Australian government must find a better way to deal with this problem. Possible solutions include immunocontraception – and scientists from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation are working on methods of genetically modifying toads so that they can produce only male offspring. If the population became overwhelmingly male, the species would eventually become extinct in Australia.
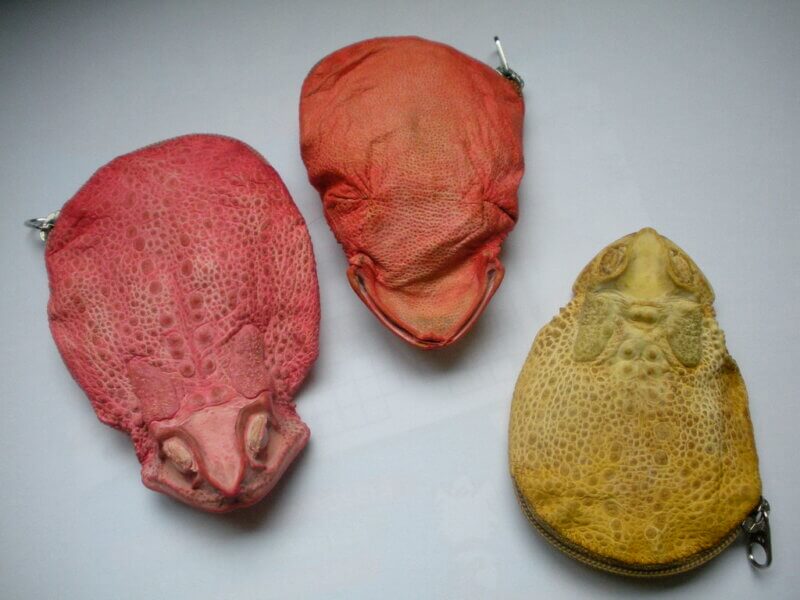
Frog and Toad Leather
Unfortunately, frog and toad leather have become novelty exotic skins. They can be exported overseas without any permits, certification, or customs clearance.
With no regulations for how the amphibians are killed – and no guarantees that those killing them can even tell the difference between a cane toad and a brown frog – buying anything made from toad leather is cruel and may contribute to the endangerment of the very animals that cane toad hunters claim to protect.
Cane Toads Feel Pain, Too
Australians have been taught to hate cane toads, making it easier to promote casual violence against them – but these amphibians feel pain and suffer the same way we all do.
Humans deliberately introduced these animals into the country, so it’s our responsibility to seek humane solutions, rather than just lashing out. Rational, scientific population-control methods are in the pipeline – methods that don’t require the cruel, dangerous, and ineffective use of golf clubs, rifles, or poison.
Animals Are Suffering in Laboratories – Help Save Them Now


